All Categories
Featured
Table of Contents
As a leading company of annuities, the status isn't a status we ever desire. We'll always remain in pursuit of much better. If you are a non-spousal recipient, you have the option to place the cash you inherited right into an inherited annuity from MassMutual Ascend! Acquired annuities may give a way for you to spread out your tax liability, while permitting your inheritance to proceed growing.
Your choice can have tax or other consequences that you may not have thought about. To help avoid shocks, we advise speaking with a tax consultant or a financial expert before you make a choice.
Taxation of inherited Joint And Survivor Annuities
Annuities do not always adhere to the exact same guidelines as various other possessions. Lots of people turn to annuities to make the most of their tax benefits, along with their special capacity to help hedge versus the monetary threat of outlasting your money. Yet when an annuity proprietor dies without ever having actually annuitized his/her plan to pay regular income, the person called as recipient has some key decisions to make.
Let's look more very closely at just how much you have to pay in taxes on an inherited annuity. For most kinds of home, revenue tax obligations on an inheritance are rather easy. The common instance includes possessions that are eligible wherefore's understood as a boost in tax basis to the date-of-death worth of the inherited building, which effectively removes any kind of built-in resources gains tax obligation liability, and gives the beneficiary a fresh start against which to determine future earnings or losses.
Fixed Annuities and beneficiary tax considerations
For annuities, the key to taxation is just how a lot the deceased individual paid to buy the annuity contract, and just how much money the dead person received from the annuity prior to death. Internal revenue service Magazine 575 states that, in basic, those acquiring annuities pay tax obligations the exact same method that the initial annuity owner would.
In that case, the tax is much easier. You'll pay tax obligation on every little thing over the price that the initial annuity proprietor paid. The quantity that represents the initial costs payment is dealt with as tax obligation basis, and for that reason excluded from gross income. There is a special exception for those that are entitled to obtain guaranteed settlements under an annuity contract. Lifetime annuities.
Over that amount, payouts are taxed. This reverses the normal regulation, and can be a huge advantage for those acquiring an annuity. Inheriting an annuity can be a lot more challenging than obtaining other residential property as a beneficiary. By recognizing special regulations, though, you can pick the least-taxed choices available in taking the money that's been delegated you.
We 'd like to hear your concerns, thoughts, and opinions on the Knowledge Center generally or this page particularly. Your input will help us aid the world spend, much better! Email us at. Thanks-- and Deceive on!.
Tax rules for inherited Period Certain Annuities
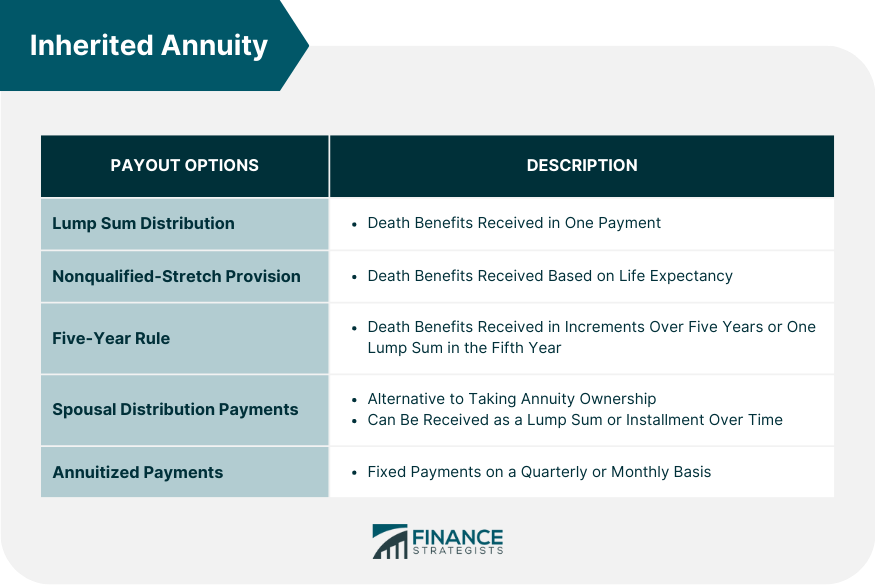
When an annuity proprietor passes away, the continuing to be annuity value is paid to people that have actually been called as beneficiaries. Variable annuities. The fatality advantage can produce an economic windfall for beneficiaries, yet it will have numerous tax obligation implications depending upon the kind of annuity and your recipient standing. The tax obligation you pay on annuity fatality benefits relies on whether you have actually a certified or non-qualified annuity.
Nonetheless, if you have a non-qualified annuity, you will not pay income taxes on the contributions portion of the distributions considering that they have already been strained; you will only pay earnings taxes on the incomes portion of the circulation. An annuity survivor benefit is a kind of repayment made to a person identified as a recipient in an annuity agreement, usually paid after the annuitant passes away.
The recipient can be a child, spouse, moms and dad, and so on. The quantity of survivor benefit payable to a recipient might be the full value of the annuity or the quantity left in the annuity at the time of the annuity proprietor's fatality. If the annuitant had started getting annuity settlements, these payments and any applicable costs are subtracted from the death profits.
In this case, the annuity would certainly provide an ensured fatality advantage to the beneficiary, despite the staying annuity equilibrium. Annuity death benefits undergo income taxes, however the tax obligations you pay depend upon how the annuity was fundedQualified and non-qualified annuities have different tax ramifications. Certified annuities are funded with pre-tax cash, and this suggests the annuity proprietor has not paid taxes on the annuity contributions.
When the survivor benefit are paid, the IRS thinks about these advantages as income and will be subject to ordinary revenue tax obligations. Non-qualified annuities are moneyed with after-tax dollars, meanings the contributions have already been exhausted, and the cash will not be subject to revenue taxes when distributed. Any kind of incomes on the annuity payments grow tax-deferred, and you will pay income taxes on the profits component of the distributions.
Taxes on Annuity Rates inheritance

They can pick to annuitize the contract and get periodic payments gradually or for the rest of their life or take a round figure repayment. Each payment alternative has various tax implications; a round figure payment has the highest tax obligation effects since the payment can push you to a higher earnings tax bracket.
You can also utilize the 5-year regulation, which allows you spread out the inherited annuity payments over 5 years; you will certainly pay tax obligations on the circulations you get each year. Recipients inheriting an annuity have several options to get annuity payments after the annuity proprietor's death. They include: The beneficiary can opt to obtain the remaining value of the annuity contract in a solitary round figure settlement.
This alternative makes use of the beneficiary's life span to identify the size of the annuity settlements. This regulation calls for beneficiaries to take out annuity repayments within 5 years. They can take several payments over the five-year duration or as a solitary lump-sum repayment, as long as they take the full withdrawal by the 5th wedding anniversary of the annuity proprietor's death.

Right here are things you can do: As an enduring spouse or a deceased annuitant, you can take ownership of the annuity and continue delighting in the tax-deferred condition of an acquired annuity. This allows you to avoid paying taxes if you keep the cash in the annuity, and you will just owe income taxes if you get annuity payments.
Nonetheless, the 1035 exchange only applies when you exchange comparable annuities. For instance, you can exchange a certified annuity for an additional qualified annuity with better functions. You can not exchange a certified annuity for a non-qualified annuity. Some annuity contracts use unique motorcyclists with an enhanced survivor benefit. This benefit is a bonus offer that will be paid to your recipients when they inherit the continuing to be equilibrium in your annuity.
Table of Contents
Latest Posts
Understanding Fixed Vs Variable Annuities A Comprehensive Guide to Choosing Between Fixed Annuity And Variable Annuity Defining Fixed Interest Annuity Vs Variable Investment Annuity Pros and Cons of V
Highlighting the Key Features of Long-Term Investments Key Insights on Your Financial Future Breaking Down the Basics of Investment Plans Benefits of Choosing the Right Financial Plan Why Retirement I
Decoding Variable Annuities Vs Fixed Annuities Key Insights on Retirement Income Fixed Vs Variable Annuity Breaking Down the Basics of Variable Annuity Vs Fixed Annuity Advantages and Disadvantages of
More
Latest Posts